- Published on
Reinforcement Learning Soccer Bot
- Authors

- Name
- Vincent Hu
Reinforcement Learning Soccer Bot: Multi-Agent Training in DeepMind Soccer Environment
Introduction
This project explores the application of reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms to train intelligent agents capable of playing soccer in a multi-agent environment. Using the DeepMind Soccer Environment from dm_control, we implemented and compared several state-of-the-art RL algorithms including SAC (Soft Actor-Critic), PPO (Proximal Policy Optimization), and POCA (Policy Optimization with Competitive Advantage) to develop autonomous soccer-playing agents.
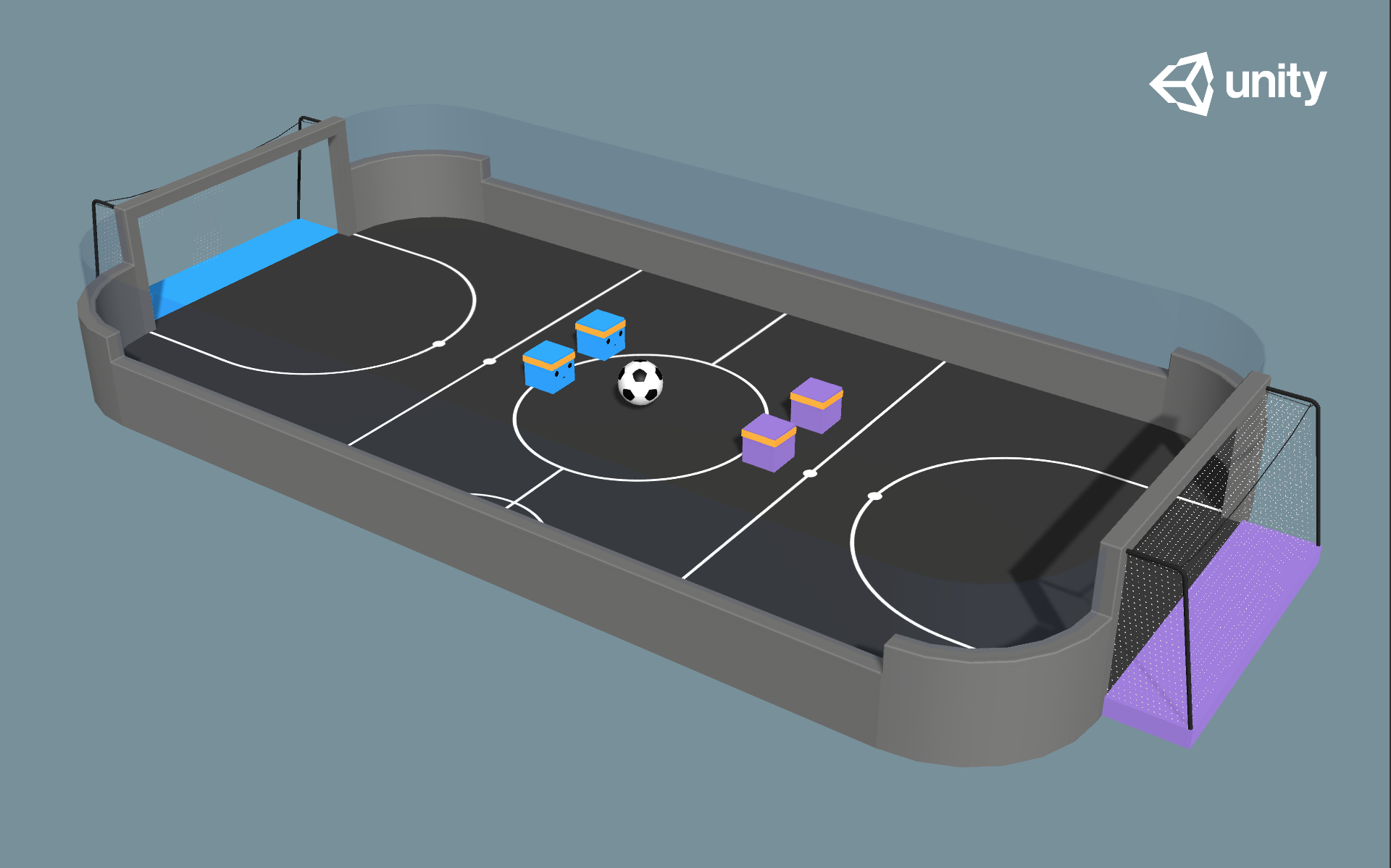
The DeepMind Soccer Environment provides a realistic physics-based simulation where agents must learn complex behaviors including locomotion, ball control, and strategic gameplay to score goals against opponents.
The Challenge
Training agents to play soccer presents several unique challenges:
- Multi-Agent Dynamics: Agents must learn to coordinate with teammates while competing against opponents
- Complex Action Space: Continuous control of multiple joints for locomotion and ball manipulation
- Sparse Rewards: Goals are rare events, requiring effective reward shaping
- Partial Observability: Agents operate in ego-centric frames, requiring spatial reasoning
- Non-Stationarity: Opponent strategies evolve during training, creating a moving target
Environment Setup
The project uses a custom wrapper around the DeepMind Soccer Environment that provides:
- 2v2 Team Configuration: Two agents per team competing on a soccer field
- Ego-Centric Observations: Ball and agent positions relative to the observing agent
- Shaped Rewards: Dense reward signals to guide learning beyond sparse goal rewards
- Flexible Policy Interface: Support for custom policies and pre-trained models
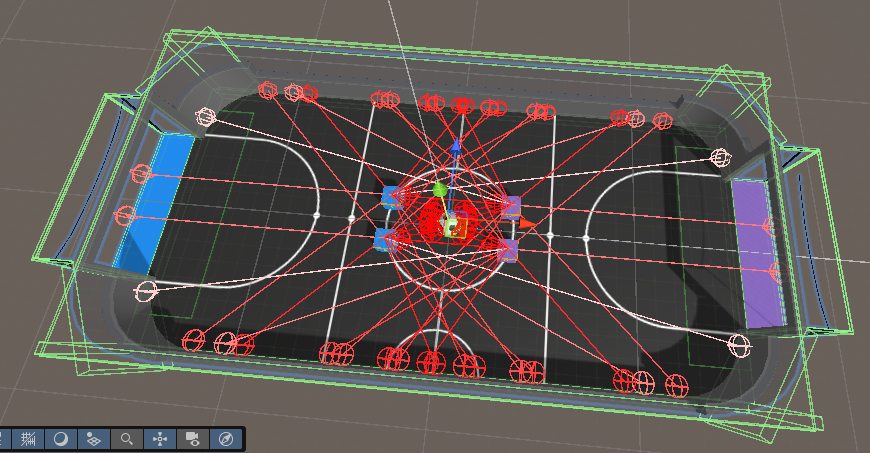
Key Environment Features
- Team Size: Configurable 2v2 matches
- Time Limit: 10-second game episodes
- Physics Simulation: Realistic MuJoCo physics engine
- Visualization: Real-time rendering for training monitoring
Algorithms Implemented
1. Soft Actor-Critic (SAC)
SAC is an off-policy algorithm that maximizes both expected return and entropy, encouraging exploration while maintaining sample efficiency.
Advantages:
- Sample-efficient off-policy learning
- Automatic temperature tuning
- Robust to hyperparameter choices
2. Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)
PPO is a policy gradient method that uses clipped objective functions to ensure stable learning. It's particularly effective for continuous control tasks and multi-agent scenarios.
Key Features:
- Clipped surrogate objective prevents large policy updates
- Multiple epochs of updates per batch
- Works well with function approximation
3. Policy Optimization with Competitive Advantage (POCA)
POCA is designed specifically for competitive multi-agent scenarios, learning policies that maximize competitive advantage over opponents.
Characteristics:
- Explicitly models opponent strategies
- Learns robust policies against diverse opponents
- Effective in zero-sum competitive settings
Training Methodology
Reward Shaping
To address the sparse reward problem, we implemented a shaped reward function with multiple components:
- Goal Reward: Large positive reward (+10) for scoring goals
- Ball Proximity: Exponential reward for being close to the ball
- Ball Possession: Extra reward when within 0.5m of the ball
- Progress to Goal: Reward for moving the ball toward the opponent's goal
- Exploration Bonus: Small reward for forward movement
Training Configuration
- Algorithm: SAC, PPO, or POCA
- Network Architecture: Multi-layer perceptron with 256-512 hidden units
- Training Episodes: Millions of environment interactions
- Evaluation: Periodic evaluation against fixed opponents
Multi-Agent Training Strategy
Since the environment is multi-agent, we employed a training strategy where:
- One agent is trained using the RL algorithm
- Other agents use fixed policies (e.g., RandomPolicy) during training
- Trained agents can be evaluated against each other or human-designed policies
Results
The trained agents demonstrate various levels of soccer-playing capability:
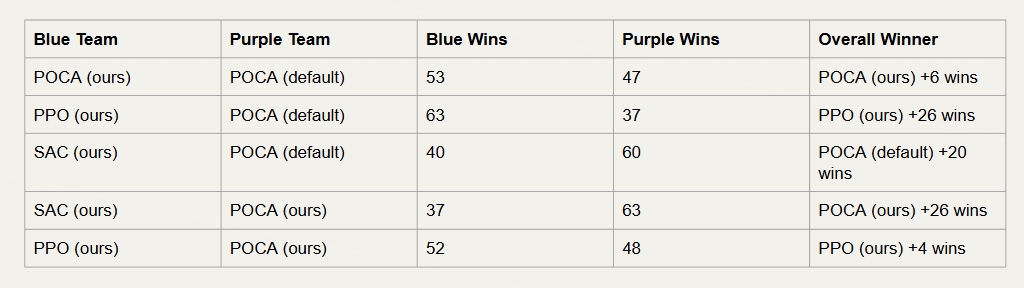
Performance Metrics
- Goal Scoring Rate: Percentage of episodes where the agent scores
- Ball Possession: Time spent controlling the ball
- Movement Efficiency: Distance traveled per goal scored
- Win Rate: Performance against baseline opponents
Observations
- SAC demonstrated sample-efficient learning but required careful hyperparameter tuning
- PPO showed stable learning with consistent improvement over training
- POCA learned competitive strategies effective against diverse opponents
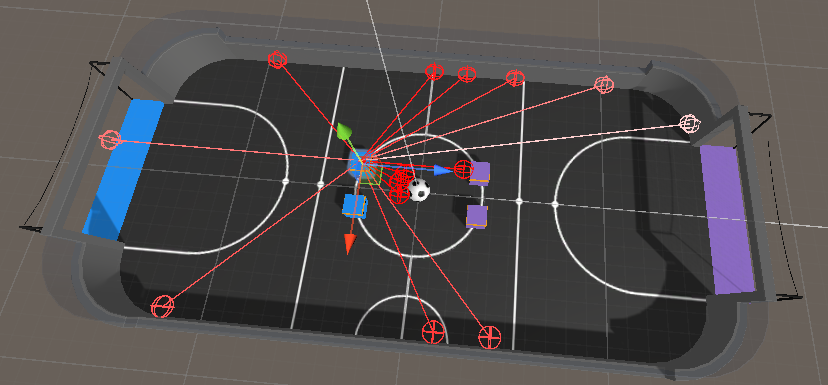
Technical Implementation
Environment Wrapper
The custom DMSoccerEnv wrapper provides a clean interface for RL training:
from dm_soccer_env import DMSoccerEnv, RandomPolicy
env = DMSoccerEnv(
team_size=2,
time_limit=10.0,
render_mode='human'
)
Training Pipeline
The training process follows a standard RL workflow:
- Environment Setup: Initialize soccer environment with specified configuration
- Policy Initialization: Create neural network policy (SAC/PPO/POCA)
- Interaction Loop: Collect trajectories through agent-environment interaction
- Policy Update: Update policy using collected experience
- Evaluation: Periodically evaluate trained policy against baselines
Integration with Stable Baselines3
The project leverages Stable Baselines3 for algorithm implementations, providing:
- Well-tested RL algorithm implementations
- Efficient vectorized environments
- Comprehensive logging and monitoring
- Model checkpointing and evaluation tools
Challenges and Solutions
Challenge 1: Sparse Rewards
Problem: Goals are rare, making it difficult for agents to learn.
Solution: Implemented dense reward shaping with multiple components to guide learning toward goal-scoring behaviors.
Challenge 2: Multi-Agent Coordination
Problem: Agents must learn to work with teammates while competing.
Solution: Trained agents individually first, then evaluated in team settings. Future work could explore joint training.
Challenge 3: Sample Efficiency
Problem: Training requires millions of environment interactions.
Solution: Used off-policy algorithms (SAC) and efficient exploration strategies to reduce sample requirements.
Future Directions
Potential improvements and extensions:
- Joint Training: Train multiple agents simultaneously with shared or competitive objectives
- Hierarchical RL: Learn high-level strategies (positioning, passing) and low-level skills (locomotion) separately
- Curriculum Learning: Gradually increase environment difficulty during training
- Transfer Learning: Pre-train on simpler tasks before soccer-specific training
Conclusion
This project successfully demonstrates the application of reinforcement learning to train soccer-playing agents in a complex multi-agent environment. By comparing different RL algorithms and implementing effective reward shaping, we developed agents capable of learning basic soccer skills including ball control, movement, and goal-scoring.
The DeepMind Soccer Environment provides an excellent testbed for multi-agent RL research, combining realistic physics simulation with the complexity of competitive team sports. The insights gained from this project contribute to understanding how RL agents can learn complex, coordinated behaviors in multi-agent settings.