- Published on
Total Recall
- Authors

- Name
- Vincent Hu
TotalRecall: A Software Framework for Capturing Events of Interest from Long Surveillance Videos
Introduction
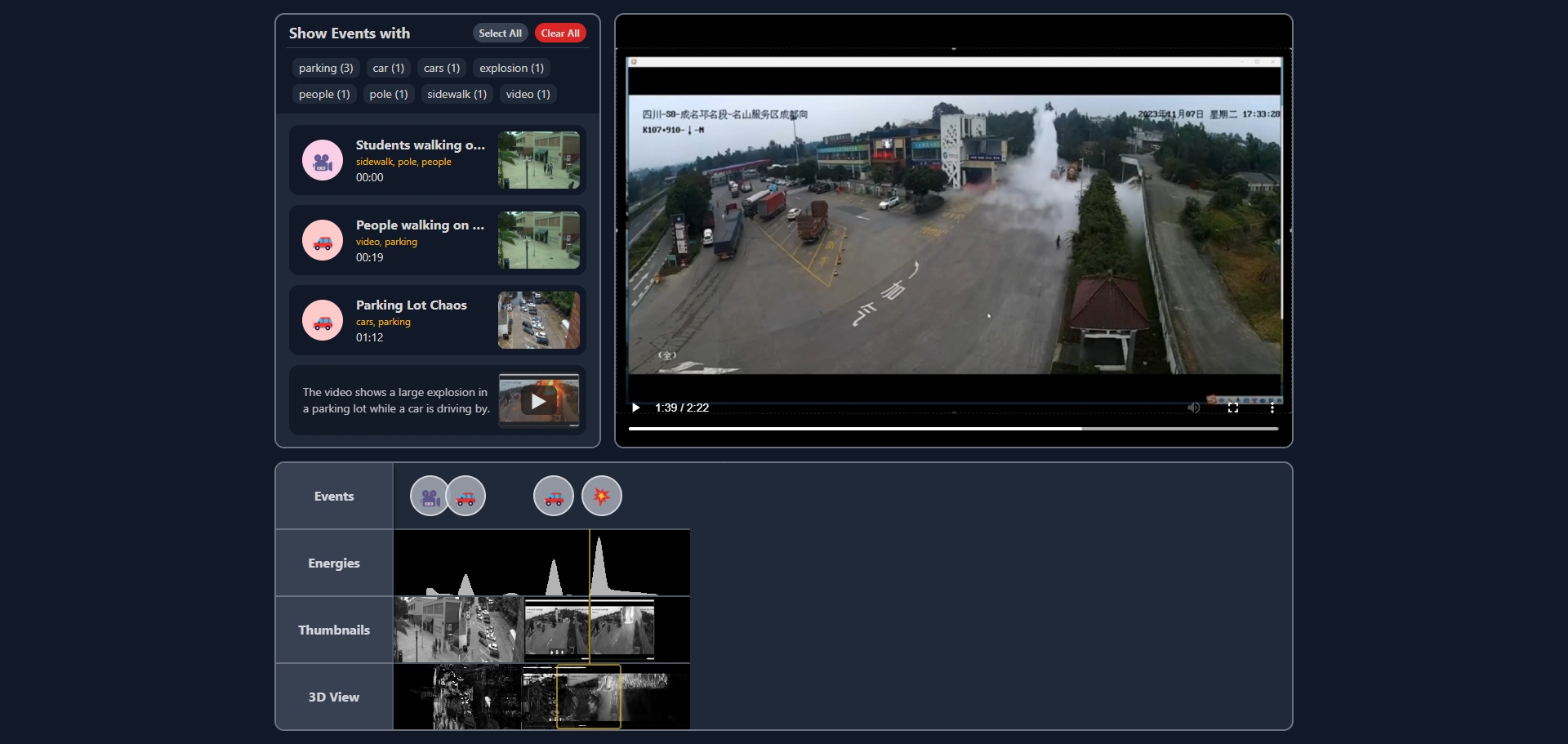 TotalRecall is an advanced software framework designed to efficiently capture and analyze events of interest from lengthy surveillance videos. Developed by Vincent Hu and Pengyu Cui, this project integrates cutting-edge AI techniques to process video data and extract meaningful insights, making it a powerful tool for automated event detection and summarization.
TotalRecall is an advanced software framework designed to efficiently capture and analyze events of interest from lengthy surveillance videos. Developed by Vincent Hu and Pengyu Cui, this project integrates cutting-edge AI techniques to process video data and extract meaningful insights, making it a powerful tool for automated event detection and summarization. The Problem
Surveillance videos generate an overwhelming amount of data, making manual review time-consuming and inefficient. Traditional monitoring methods lack the ability to automatically identify key moments, leading to missed events and inefficient security operations. TotalRecall addresses this challenge by leveraging AI models to automate the detection and captioning of significant events.
Architecture
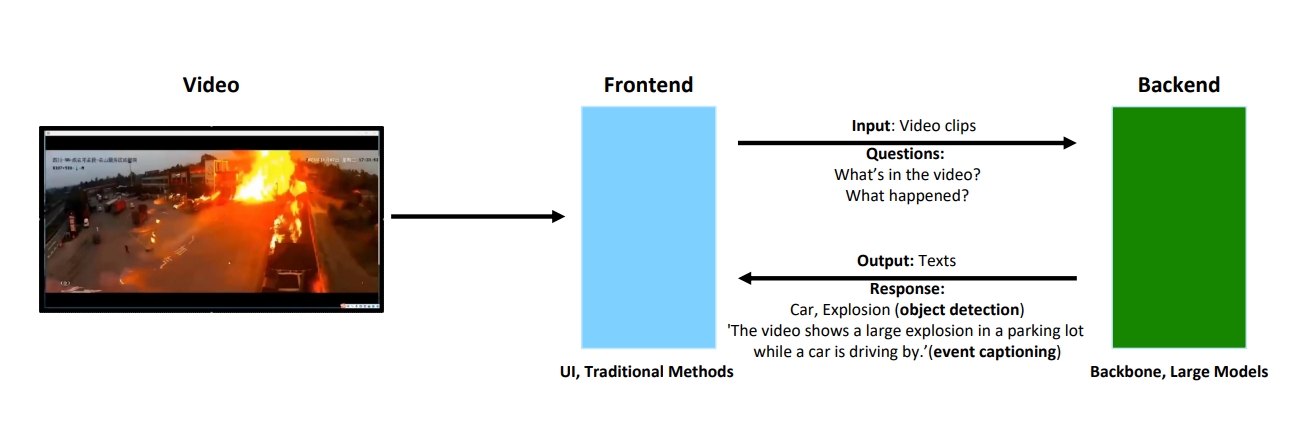 The TotalRecall framework consists of a frontend and a backend, working together to process video input and generate meaningful textual descriptions of detected events.
The TotalRecall framework consists of a frontend and a backend, working together to process video input and generate meaningful textual descriptions of detected events. - Frontend: Responsible for UI display and visualization of detected events, allowing users to navigate and review critical moments efficiently.
- Backend: Performs event detection and captioning using state-of-the-art AI models, including Florence-2 and LLaVa-Next-Video, ensuring accurate and efficient processing.
Key Features
- Event Detection: Identifies key objects and actions in video clips, answering fundamental questions like “What’s in the video?” and “What happened?”.

Frame Difference Analysis: Uses a baseline method to detect changes between frames and segment events. The model visualizes results using an progress bar with energy, inspired by Youtube Video. An energy bar represents how significant an event is, based on the magnitude of detected motion or the rarity of an object appearing in the scene.
- Multi-Model Processing:
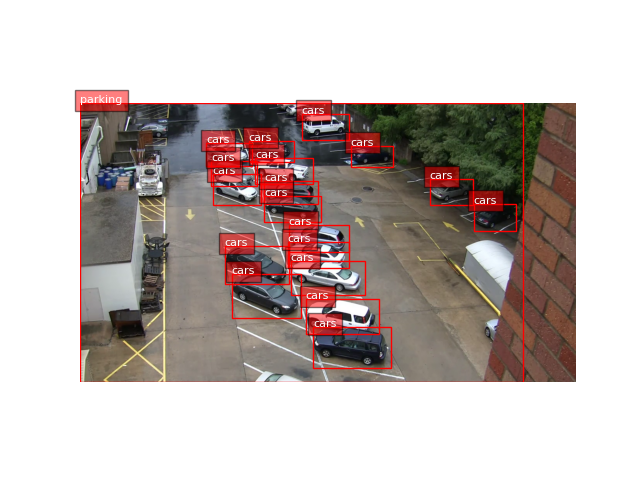

- Florence-2: Provides a unified representation for various vision tasks, improving event recognition.
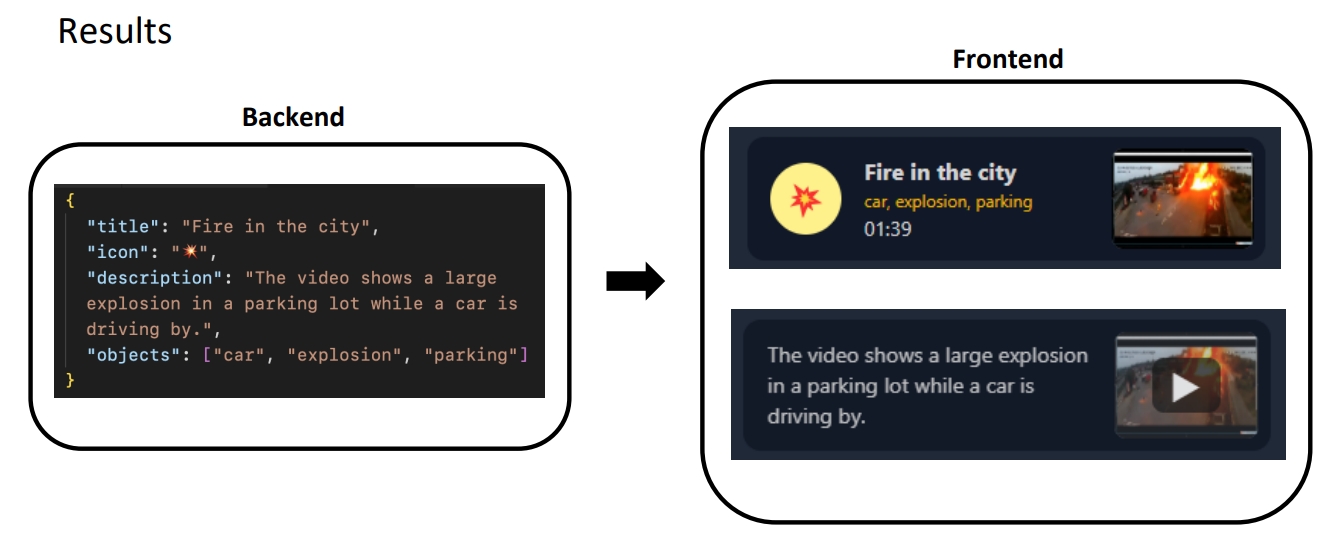
- LLaVa-Next-Video: A fine-tuned model with strong zero-shot video understanding capabilities, capable of processing long videos efficiently.
GIS Integration: Incorporates geospatial information for location-based event analysis, making it particularly useful for surveillance applications requiring geographic context.
Efficient Video Summarization: Converts long surveillance videos into structured event logs with descriptions, icons, and categorized event types.
Workflow
- Video clips are processed through a frame processor to identify significant changes.
- Detected objects and events are labeled, and a customized prompt is used to generate event descriptions.
- AI models refine the event summaries, generating structured outputs with event type, title, and description.
- The frontend displays event logs for user interaction, visualization, and review.
Results
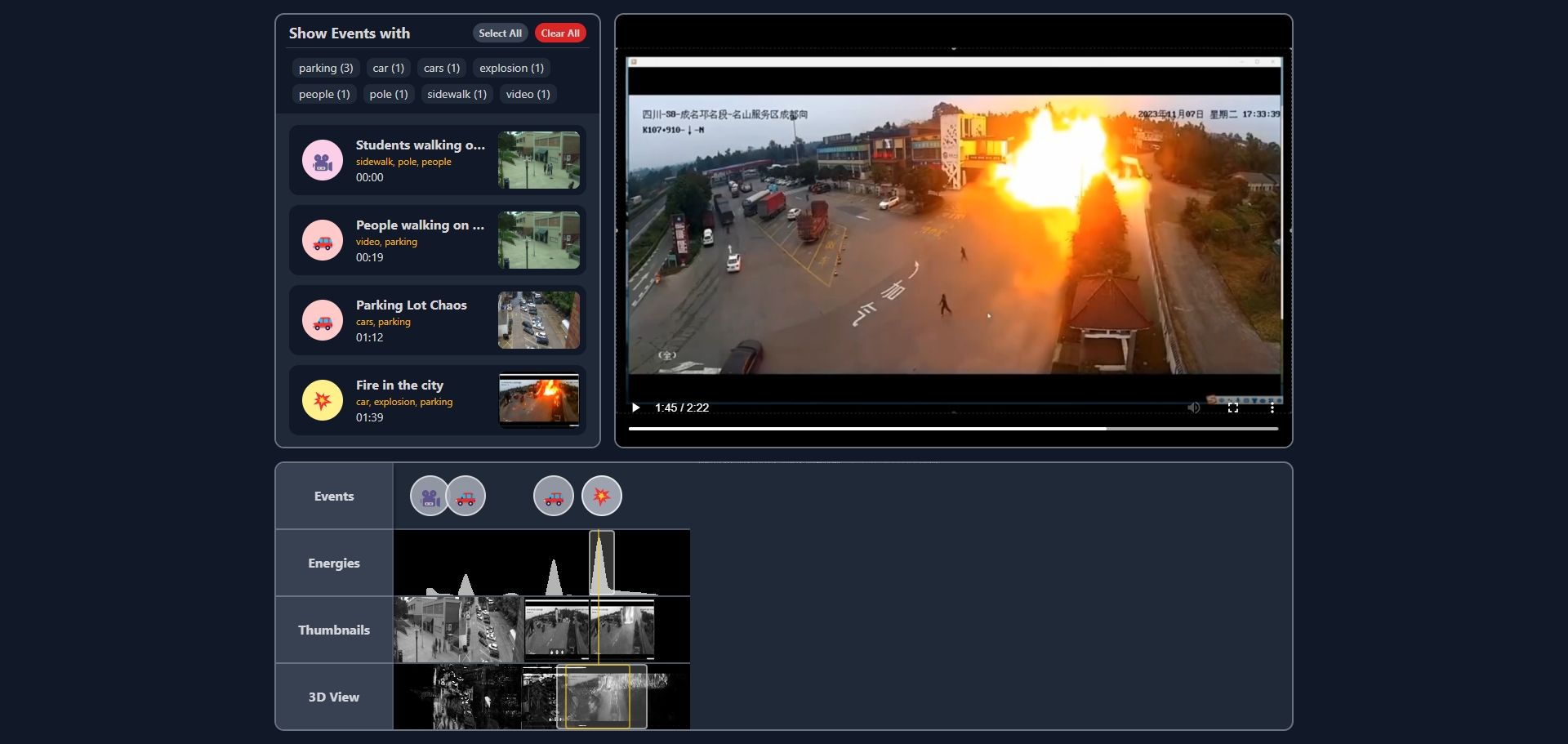 TotalRecall effectively extracts meaningful events from surveillance footage, presenting them in an organized and accessible format. The integration of advanced AI models significantly improves video understanding, making the framework a valuable asset for security, traffic monitoring, and automated video analysis applications.
TotalRecall effectively extracts meaningful events from surveillance footage, presenting them in an organized and accessible format. The integration of advanced AI models significantly improves video understanding, making the framework a valuable asset for security, traffic monitoring, and automated video analysis applications. Limitations
Despite its success, TotalRecall faces some challenges:
- Processing Speed: AI-driven analysis can be computationally intensive.
- Visualization: Enhancing user-friendly representations of results remains an ongoing goal.
- Accuracy: Event detection performance depends on training data and model refinement.
Conclusion
TotalRecall represents a significant step forward in automated video surveillance analysis. By combining deep learning with GIS integration, it offers a scalable and efficient solution for detecting, captioning, and summarizing events in long surveillance videos. As the framework continues to evolve, improvements in speed, visualization, and accuracy will further enhance its capabilities.